Every supplier, manufacturer, and OEM plays a role in ensuring the integrity of the components they order. It’s never enough to leave it to upstream partners in the supply chain. Components change hands many times on their way to the end product, leaving multiple potential entry points for bad parts.
Advanced component testing techniques are a key defense against defective, substandard, mislabeled, and inauthentic components — and a protection for your investment. Here are a few of the advanced testing capabilities that we use at Sensible Micro to verify quality and detect anomalies.
1. Low Power Electrical Testing
This technique is important if there is any concern or possibility that powering on a component could result in damage. Not all components actually need to be fully powered up to be examined. Low power testing applies current-limited sine-wave voltage that tricks the part into thinking it’s being properly powered up in order to get the signature reading (or some other measurement).
Our electrical analysis capabilities at Sensible Micro revolve around low power electrical confirmations since they are the safest way to conduct electrical testing of components. Electronic components such as batteries, capacitors, chokes, crystals, diodes, fuses, op-amps, switches, and many others can be subjected to low power electrical testing.
2. Curve Trace Analysis
Curve tracing is a specialized electronic component testing method that analyzes the current-voltage characteristic (or I-V curve) of a circuit. The chart of the component’s performance is a visual curve, the shape of which reveals operating properties and flaws.
Sensible Micro uses an ABI Sentry V/I Signature Curve trace to find electronically-damaged pins or detect ESD damage on components. With this curve trace technique, we can also identify issues such as missing or incorrect dies, a lack of wire bonds, or inaccurate pinouts.
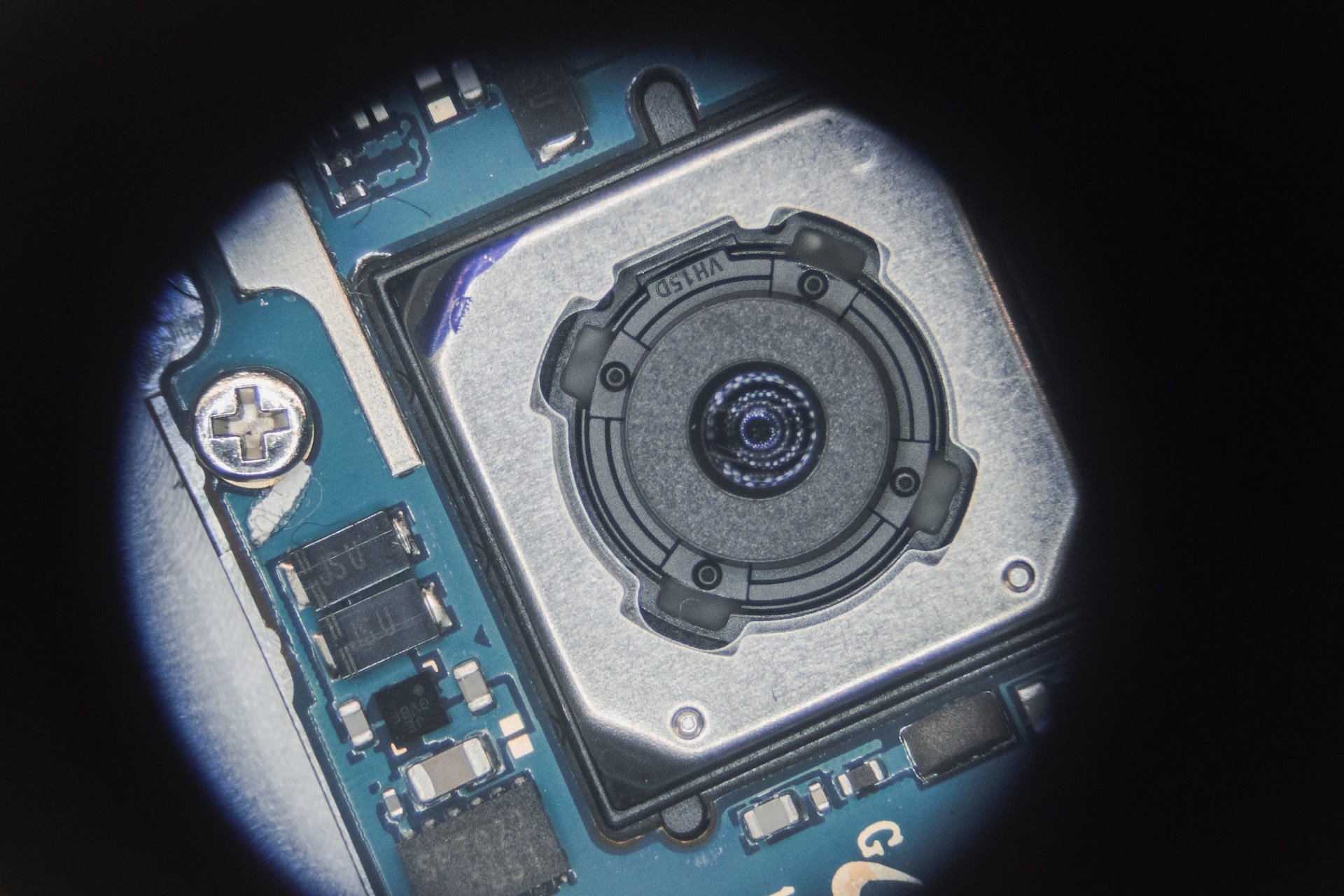
3. High Power Microscopy
Microscopy is a non-destructive method of inspecting components for material flaws, locating failure mechanisms, and comparing against a golden sample. When it’s termed “high power,” this typically means a magnification range exceeding 50X (and our capabilities at Sensible Micro actually extend upward to 1000X).
Magnification is used to generate high-res imagery and depth-of-field photography. Particularly useful for surface and lead inspections, this is a critical tool to have in any advanced component testing toolbox.
4. Marking Permanency
A combination of basic scrape tests and swabbing with mineral spirits, alcohol, or acetone can reveal anomalies of surface integrity, re-marks, blacktopping, and other problems with a component’s surface. Marking permanency tests are a useful method for identifying counterfeit components that have been re-labeled to conceal their origin.
5. XRF Analysis
XRF (X-Ray Fluorescence) analysis is an analytical technique for testing printed circuit boards (PCB), integrated circuits (IC), and individual electronic components and determining their elemental composition.
This can be effective on standard, de-lidded, or decapsulated electronic components and serves both to check for counterfeits and to detect potential hazardous materials. As a fast, non-destructive method of testing, it’s also required by many industry standards (such as AS6081) for things like lead finishing evaluation.
Advanced Component Testing With Sensible Micro
Sensible Micro is prepared to assist you in the development of a custom test regimen that suits your precise end-use requirements. Whether you’re in need of simple quality assurance tests such as solderability screenings or a full-scale General Counterfeit Avoidance Test (GCAT), our fully outfitted in-house lab is ready to help. Get in touch today!